

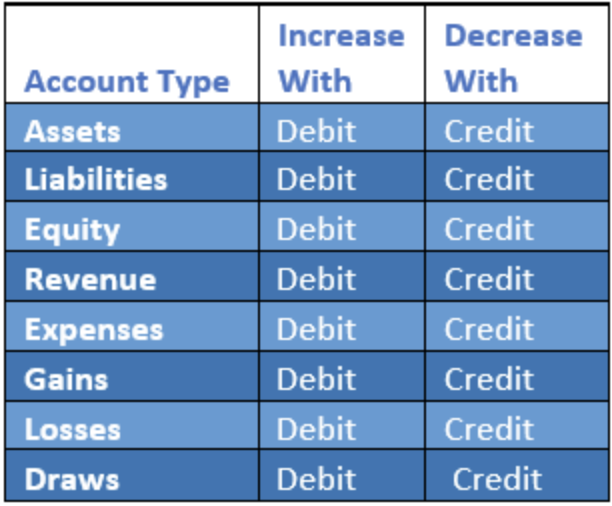
Related: 12 Widely Accepted Accounting Principles Debits and credits in everyday business accounting transactions Here's a table that outlines the way each debit and credit affects the accounts they're added to: The reason why debits and credits affect accounts differently is due to their accounting equations that are underlying and every accounting transaction begins with the basic accounting equation : If the account is unbalanced, then it will not be accepted by accounting software. In a transaction, each amount of debits is required to be equal to the sum amount of credits. This rule is consistent with accounts such as revenues, liabilities and equity. When accounts have a credit balance, the amount increases when a credit is applied to them and is lowered when a debit is applied to them. The rule is consistent with accounts such as expenses, assets, and dividends. When a debt is added to a debit balance, it typically increases the amount in all accounts and the amount is lowered when a credit is applied to them. Here are the rules that govern the usage of credit and debit in accounting: Related: Learn About Being An Accountant Debit and credit rules Liabilities : The amounts a business owes to another business, person or bankĮquity: A business's assets subtracted by liabilities Here are the common accounts that can be affected by debits and credits:Įxpenses : Any business operations costs that occur such as wages or suppliesĪssets: Items that a company owns that have economic value and can be sold for a cash value, such as property, vehicles or land Before you can understand the way debits and credits work in accounting, you must first understand the accounts that are affected by debit and credit transactions. In order for financial statements to be accurate, each debit and credit must be balanced and have an equal number of recordings on the accounts that they affect. A debit is recorded on one account and a credit is recorded on another account. There is no limit to the number of accounts that can be affected by a transaction, but at least two accounts will always be affected. credit accountingĮvery time an accounting transaction is made, at least two accounts are affected. Related: Your Guide to Careers in Finance Debit vs. These accounts are usually increased with a credit: Credits are added to the right side of T-accounts in double-entry bookkeeping methods. Private Accounting: Definition and Key Differences What is a credit in accounting?Ī credit is a record in accounting entries that will either decrease an asset or expense account or increase a liability or equity account. These accounts are usually increased with a debit: Debits are added to the left side of T-accounts in double-entry bookkeeping methods and are considered the opposite of accounting credits. In business, accounting debits can lead to a decrease in liabilities or an increase in assets. What is a debit in accounting?Ī debit is a record in personal accounting that represents the money that flows into an account.
#DEBIT CREDIT TABLE PLUS#
In this article, we discuss what debits and credits are in accounting, plus offer examples of each.
Learning the details between the money coming into your account and funds going out-can help you keep your business records accurate and give you a better idea of your company's financial standing. The basics of debits and credits in accounting are important to know, especially for small businesses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
